Browser Fingerprinting is a tracking technique that collects information about the user’s browser configuration to create a unique “fingerprint” that can identify and track the user across websites, even without cookies.
-
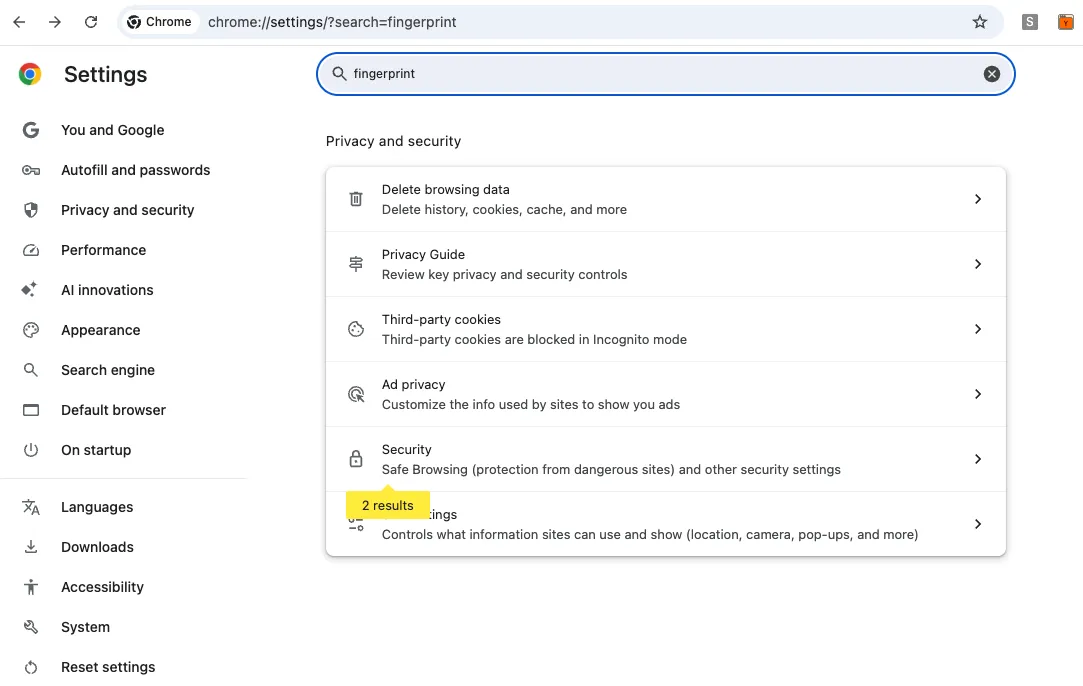
Chrome offers very little built-in protection against fingerprinting. Users have to rely on extensions to prevent it. Interestingly, when I searched for ‘fingerprint’ in Chrome settings, it showed that there are two results, but when I go into those settings, there is no mention of fingerprint.
-
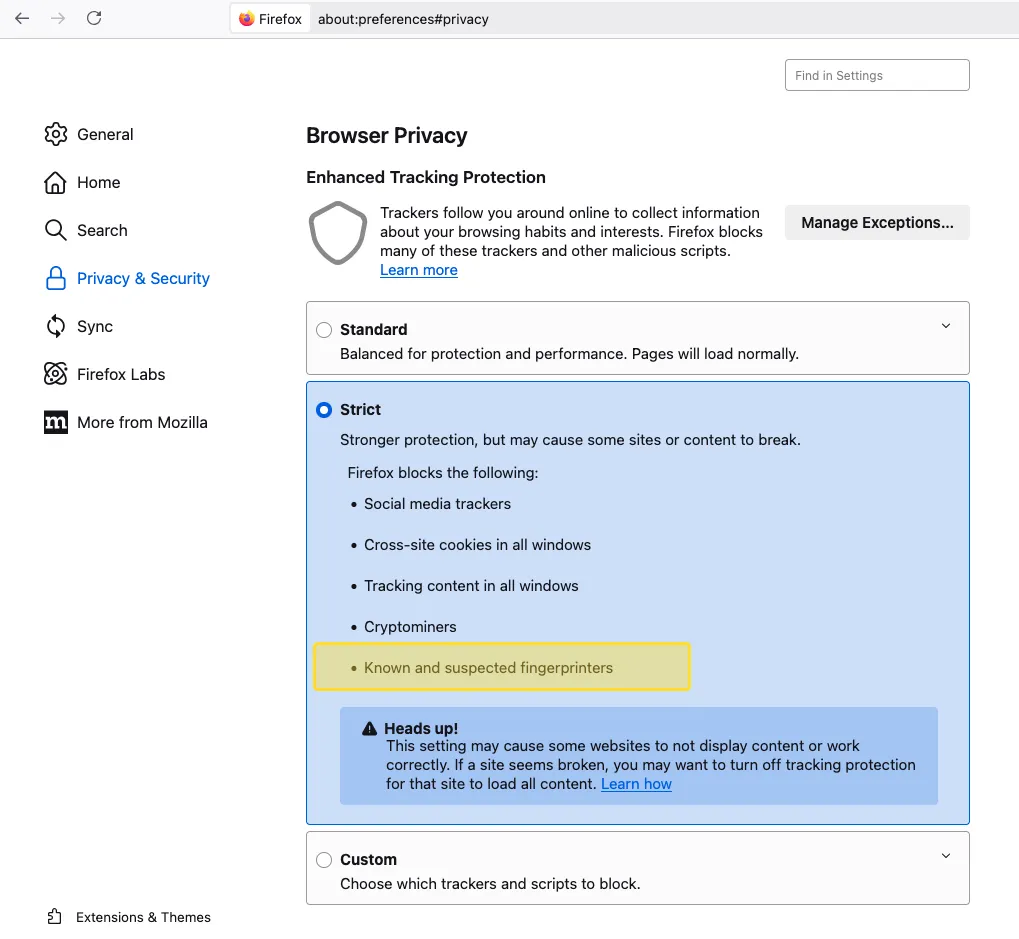
Firefox offers Enhanced Tracking Protection with three protection levels, of which Strict level prevents known and suspected fingerprinters in addition to blocking cross-site cookies, tracking content in all windows etc.
-
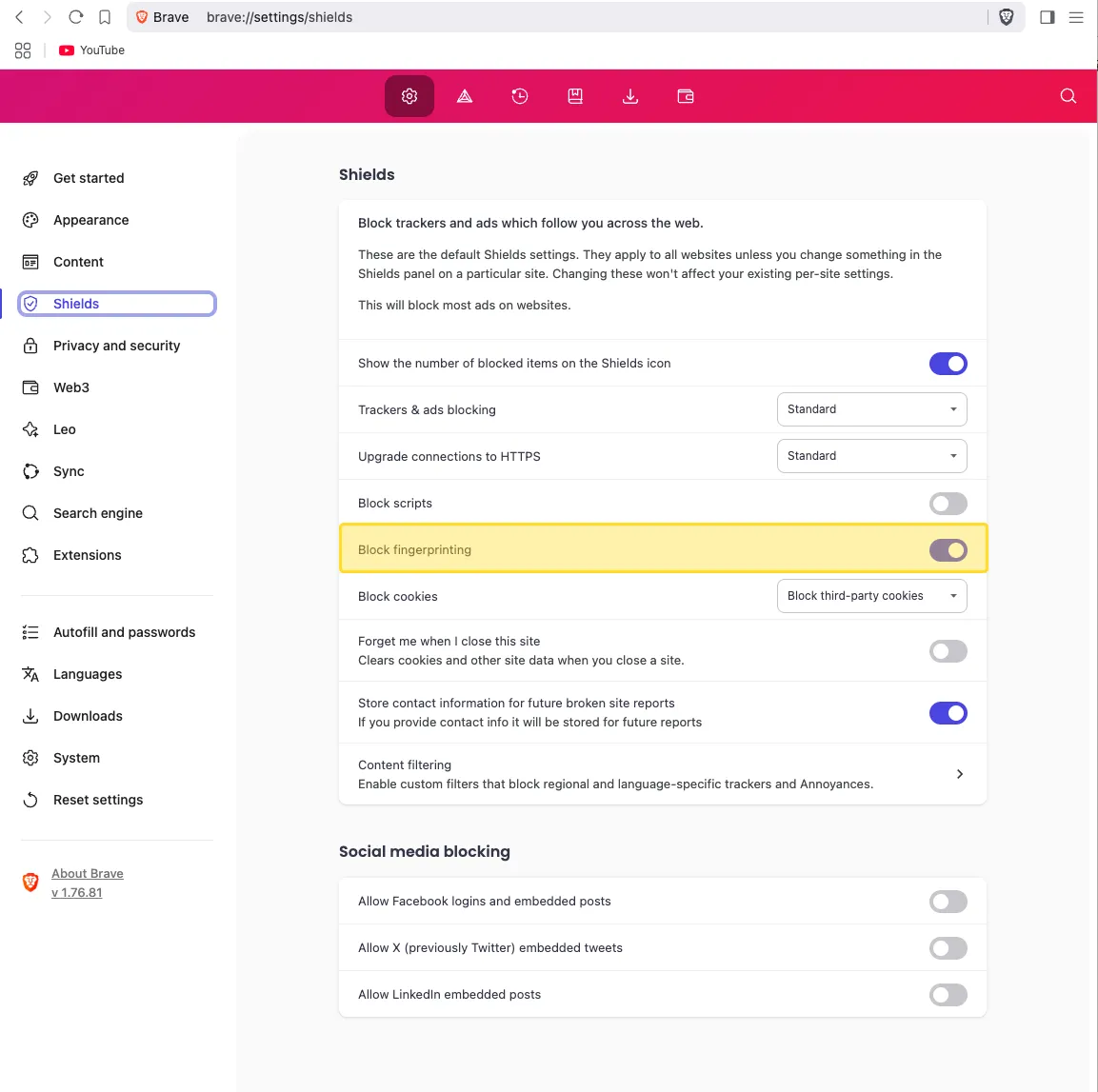
Brave enables fingerprinting protection by default. You see the pattern here - privacy-first approach. It can be turned off Settings > Shields. Its protection approach (“privacy through randomization”) is considered quite strong among mainstream browsers.
Here are the screenshots of the settings in each browser
Chrome configuration
Firefox configuration
Brave configuration